In this blog we are going to look at Product Catalog management (PCM) and what all the capabilities that PCM has, Data model overview and key guardrails.

About PCM and its role in RLM:
PCM is going to be the center of product-to-cash journey. It’s internally integrated with RLM modules out of the box, where you need product and its related information like CPQ that we have seen (like transaction management, configurator, pricing management). Every RLM module is pre-integrated with PCM, and even customers — they can use their legacy data to PCM, create PCM as one master body of information.
At the same time, they can also distribute their information to sales channels, service channels, even with third-party systems using our APIs.

Introduction of PCM and its capabilities:
With sprint 24, Salesforce officially introduced PCM to the customers. How to build PCM easily and manage product & its related information. This whole PCM comes with different capabilities like dynamic attribute, product bundling, classification rules, and many more capabilities which make more easy to use and to define entire product definition in one single place and you’ll also notice salesforce designed it customer friendly. You can even build complex product definition in one single place. All of that is to put customer on top of the market and they should be able to be competitive and they can manage their business easily.
More on PCM:
PCM is catalog-driven quoting & ordering solution across channels. It completely built on core. This is going to be foundational feature for all other industries in Salesforce. For every industry who wants to use product they are going to use the foundational feature as PCM. PCM is centralized platform to define and launch products faster. It is going to empower catalog-driven selling & fulfillment which is going to minimize the errors during sales and service process because all the information of products placed in one single place and is not distributed with other systems (or) offline systems or different online systems. With PCM customers stay on top, agile, they can maintain with product definition easily.
Key Features of PCM:
Introducing the Product Designer Home
One of the first features in PCM is the Product Designer Home. Every application needs a central place where users can begin their work, and the Designer Home serves as that starting point for PCM. Here, users will find all essential links in one place, allowing seamless navigation across different sections directly from Designer Home.
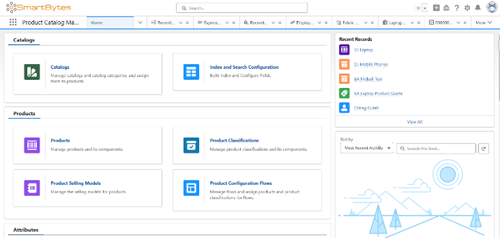
Structure of the Designer Home
The Designer Home is organized into four main sections:
- Catalog
- Product
- Attribute
- Rules
This out-of-the-box setup provides a structured and intuitive navigation experience for users. Moreover, customers can customize the Designer Home to add additional quick links as needed, making it an even more versatile tool. This setup provides users with quick and easy access to essential resources, enhancing their overall experience.
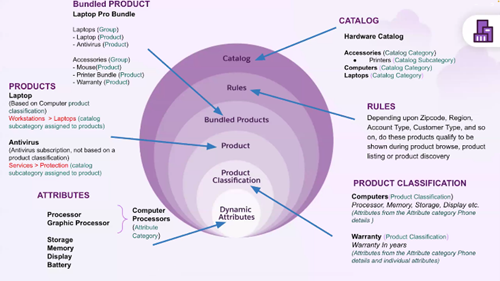
Catalog and Categories:
The next feature we have in PCM is Catalog and Categories. This feature allows users to organize and structure their products in a way that creates an effective and accessible hierarchy. By defining products within a catalog and further grouping them into categories, PCM provides a clear overall organization, making it easier for customers to manage and navigate their product offerings.
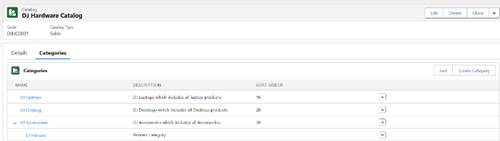
Understanding Catalogs
A Catalog is essentially a comprehensive listing of all products or services available for sale. This structured list gives customers an organized view of all their offerings, much like a traditional catalog. Within PCM, the catalog helps users keep a centralized repository of products that can be further refined and segmented for different business needs.
Using Categories and Subcategories
Categories allow further classification within the catalog, enabling customers to organize products into specific groups. These groups can then be broken down into subcategories, creating a hierarchy that caters to diverse product lines and sales channels. This categorization is beneficial for businesses with varied product offerings, as it helps streamline the sales and ordering processes.
For example, let’s say you are a furniture retailer selling both office and domestic furniture. Under Domestic Furniture, you might have categories such as Dining Room Furniture, Living Room Furniture, and Customized Furniture. Each of these categories can then contain specific product lines tailored to meet different customer needs. This Catalog and Categories structure in PCM empowers businesses to create an organized, intuitive product hierarchy, making it easier to manage their products, tailor their sales strategy, and enhance the customer experience across different channels and markets.
Attributes and Attribute Categories
In PCM, every product has certain Attributes that help define its specific characteristics. Attributes represent the unique traits or features of a product, giving it identity and making it easier for users to understand its functionality. This attribute-based approach allows businesses to set up details that apply to a range of products, providing flexibility and precision.
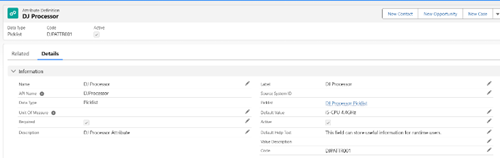
Understanding Attributes
An Attribute is a characteristic or capability assigned to a product. By defining attributes, you can specify details about a product once and reuse them across multiple products. This decoupled approach makes it easy to apply common traits or specifications without the need to duplicate information across products. With PCM, attributes are managed in a way that allows you to select which specific attributes are relevant for each product. This flexibility ensures that only relevant attributes are displayed, helping to streamline the product setup process.
Attribute Categories
Attribute Categories enable logical grouping of attributes, making it easier to organize and manage them. For instance, if you want certain physical attributes to be shown during product selection at runtime, you can create an attribute category (such as “Physical Attributes”) and assign relevant attributes to this category. You can then apply the attribute category to a product, ensuring that these grouped attributes appear at the right time during the sales process.
Product Classification
Product Classification in PCM is a feature designed to streamline and improve the accuracy of product creation. It allows businesses to create predefined templates by organizing attributes into a structured format, which can then be applied to products. This approach provides consistency across products and speeds up the setup process, reducing the risk of errors.
Key Benefits of Product Classification
Enhanced Accuracy
By using templates to define product characteristics, businesses ensure that each product adheres to a standardized structure. This accuracy is crucial for maintaining data integrity across a large catalog of products.
Efficiency in Product Setup
With templates ready to go, users can quickly assign attributes to new products, saving time and minimizing repetitive work. Product Classification automates the assignment of attributes, ensuring that all relevant characteristics are defined for each product without needing manual input every time.
Trust and Reliability
A well-structured classification system builds trust in the accuracy and completeness of product data. This systematized approach means businesses can rely on their catalog’s information for accurate quoting, ordering, and reporting processes
Flexibility and Scalability
Product Classification is adaptable to various industries and product types, making it a versatile solution for businesses with diverse offerings. As your catalog grows, templates can be modified or expanded, ensuring that your product management system scales with your business.
By using Product Classification in PCM, businesses gain a powerful tool for creating, managing, and organizing products effectively. This feature not only enhances accuracy and efficiency but also ensures that each product is consistently defined, building a reliable foundation for sales, service, and customer satisfaction.
Product Definition
In Salesforce, product offerings are structured into two main types:
- Simple Products: These are standalone products with no parent or child relationships. They exist independently in the catalog and are straightforward to add to quotes.
- Bundle Products: These products have hierarchical relationships, either as parent products with child components or as part of a group. Bundles are ideal for packaging related products together for streamlined sales.
Within these product types, there are two configuration options in RLM:
- Configurable Products: These allow sales representatives to make adjustments and customizations during the quoting process. This flexibility helps tailor offerings to meet specific customer needs in real time.
- Static Products: Unlike configurable products, static products do not allow any additional configuration once they are defined. They remain fixed and cannot be altered during the sales process.
This structure provides businesses with the flexibility to offer both adaptable and fixed product options, catering to a wide range of customer requirements.
Qualification Rules and Their Role in Product Eligibility
In Salesforce CPQ, Qualification Rules help define the criteria under which customers are eligible to purchase specific products. These rules are based on defined conditions that determine whether a product can be offered to a customer. Qualification rules are powered by the Business Rules Engine (BRE), which efficiently processes the conditions and makes real-time decisions on product eligibility.
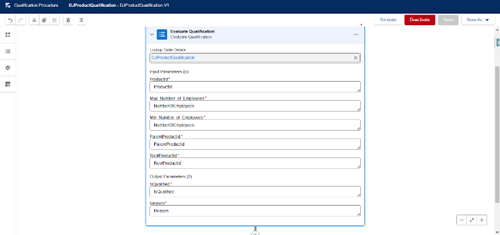
Understanding Qualification Rules
A Qualification Rule is a set of conditions used to determine whether a customer is eligible to purchase a particular product. These rules help ensure that only the appropriate products are available to the customer based on factors like customer profile, subscription details, or other criteria.
Qualification rules are defined during design time, but their execution occurs at runtime, meaning they are evaluated when the user is interacting with the CPQ system. By default, all products are considered eligible, but once the conditions defined in the qualification rules are applied, the system will either qualify or disqualify the product.
How Qualification Rules Work
- Business Rules Engine: The qualification rules are powered by a high-performance Business Rules Engine (BRE), which processes decision tables and qualification procedures to assess whether the product is qualified or not.
- Decision Tables: You can define your qualification rules in Decision Tables (DT). These tables map conditions to outcomes, allowing you to control how the rules are applied based on the customer’s data or quote details. The orchestration of these rules can be managed from one or multiple decision tables, providing flexibility in defining complex eligibility criteria.
- Qualification Procedures: The qualification rules are structured through qualification procedures. These procedures ensure that the rules are applied in a specific sequence, helping to control the logic flow and determine whether the product meets the qualifications based on the defined conditions.
- Runtime Execution: While the qualification rules are defined during design time, they are executed at runtime. When a customer selects products, the conditions are checked against the qualification rules, and based on the matching criteria, the products are either qualified or disqualified.
- Category-Specific Rules: Qualification rules can be applied to specific product categories, ensuring that eligibility is checked not just on individual products but across entire categories of items. This allows for more granular control over which products are available in certain scenarios.
Specification Type and Its Role in Salesforce
Specification Type is a new concept introduced in Salesforce to support Record Lifecycle Management (RLM) across all industries. This feature allows businesses to align their product terminology with the specific language used within their industry. Different industries often have unique terms for similar products, and Specification Type provides a way to bridge this gap and maintain consistency across various use cases.
Understanding Specification Type
A Specification Type is a customizable term used to represent different product categories or terminologies that vary by industry. For example, in Salesforce, we commonly refer to “products,” but in other industries, the terminology may differ:
- Medical Industry: Products might be referred to as “Kits” or “Packs.”
- Insurance Industry: Products might be categorized as “Auto Insurance,” “Health Insurance,” etc.
How Specification Type Works
- Industry-Specific Terminology:Salesforce allows businesses to customize their product categories and terminology using Specification Types. This ensures that product names and categories align with industry-specific needs, providing a consistent and user-friendly experience for customers and partners.
- Integration with Record Types:Specification Types are used in conjunction with Record Types in Salesforce. Record Types allow you to define different sets of business processes, page layouts, and picklist values for various types of records.
By mapping a Specification Type to a particular Record Type, the appropriate terminology will be populated on the product record, ensuring that it aligns with the industry-specific naming conventions. - Data Model Framework:Salesforce provides a flexible data model framework that allows you to define,
manage, and apply Specification Types across different products, ensuring that each industry can implement its preferred terminology.
List of the APIs:
These are the APIs that are there in Salesforce RLM.

Conclusion
The features of Revenue Lifecycle Management (RLM) in Salesforce, including Product Designer Home,
Catalog and Categories, Attributes and Attribute Categories, Product Classification, Product Definition, Qualification Rules, and Specification Type.
provide a comprehensive framework for businesses to efficiently manage their products, define eligibility criteria, and streamline the entire product lifecycle.
By leveraging these tools, organizations can ensure that their products are properly structured, aligned with industry-specific needs, and offered to customers based on defined qualifications,
ultimately optimizing the sales process and driving revenue growth.
